Thermal Imaging for Medical and Veterinarian Applications
Medical thermography is an accurate, quantifiable, non-contact, non-invasive, diagnostic technique that allows the examiner to visualise and quantify changes in skin surface temperature using high performance infrared cameras.
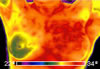

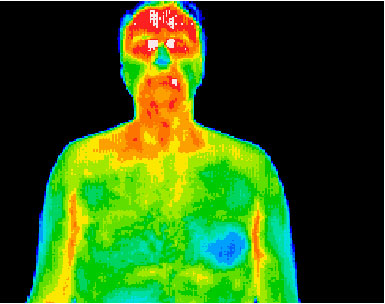
FLIR thermal cameras are the leading choice in clinical, veterinarian and research medicine, proven to be highly accurate, reliable and easy to use.
Medical Applications
Infrared thermography is based on analysis of skin surface temperatures as a reflection of normal or abnormal human physiology using a high performance infrared camera. The camera generates images with thermal data in real time and in a fraction of a second, a large area of the human body can be imaged and dynamic responses to stimuli are easily documented.
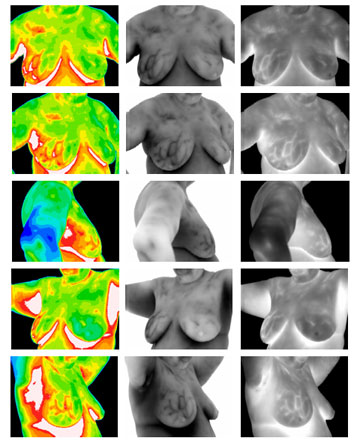
Today, infrared thermography has become one of the most efficient techniques for the study of skin temperature. High performance, infrared cameras provide a sensitive diagnostic tool for a multitude of clinical and experimental situations, ranging from breast cancer screening to open heart surgery.
IR for Medical Diagnostics
Thirty years of clinical use and more than 8,000 peer-reviewed studies in the medical literature have established thermography as a safe and effective means to examine the human body. It is completely non-invasive, and as such does not require the use of radiation or other potentially harmful elements. Medical research has shown thermography to be a useful tool in research as well as being helpful in the diagnosis of Breast Cancer, Nervous System Disorders, Metabolic Disorders, Neck and Back Problems, Pain Syndromes, Arthritis, Vascular Disorders, and Soft Tissue Injuries among others.
Many base line thermographic studies have been performed which show the anticipated normal pattern of temperature in a thermal image, both in steady state as well as dynamic situations, as for example during skin heating and cooling. Characteristic changes in the normal pattern are associated with different pathological phenomena. These changes provide the basis to be able to carry out objective non-invasive investigations, which are of diagnostic value.
Veterinarian Applications

An animal’s body creates heat so it can survive. That heat fluctuates throughout the body depending on blood flow. Blood flow, to some degree, is regulated by need; for example, injured tissues need more blood to bring in more helpful cells and take away the debris of repair. The body’s recognition of injury and a subsequent increase in blood flow can happen even before the animal shows signs of pain, such as lameness.
The infrared heat that an animal emits from its body can be “viewed” with an infrared camera. The heat patterns that can be seen show a trained practitioner how the blood flow is normal, or abnormal, in a particular animal. Blood flow can be either increased or decreased, both indications of health problems.
Physiologic imaging is a function of metabolic action. Physiologic images can change and might appear prior to anatomic disruption. Thermography (or thermal imaging) is considered physiologic imaging because as the animal’s metabolism changes. For example a sore tendon heats up, that fact can be discerned.
Equine thermography
Thermography is a qualitative assessment of temperatures. The infrared camera measures temperature automatically and shows an thermal image with different colors for different temperatures. A “hot spot” indicates inflammation or increased circulation. Hot spots generally are seen in the skin directly overlying injury. A cold spot is a reduction in blood supply usually due to swelling, thrombosis, or scar tissue.
There can be “artifacts” found when using a thermography camera, so experience is a key to diagnosis. If legs have been wrapped, or blisters or liniments have been used, they will show up as areas with increased heat. Thermal symmetry is the rule – you compare one anatomic area with the same area on the other side (i.e., outside foreleg to outside foreleg).
Inflammation
Thermography can be used to determine if there is inflammation in an area that was sore on palpation, or to detect an area of increased blood flow when there is no specific pain or signs (subclinical inflammation). Most horses don’t have just one problem associated with lameness. Thermography also helps in detecting the secondary areas with problems.
It has been noted that tendons and joints will show inflammatory changes as much as two weeks before clinical lameness is apparent.
Muscle injury
A very valuable use of thermography is in detecting muscle injury. It locates the area of inflammation associated with a muscle or muscle group. It shows atrophy before it becomes apparent clinically. Atrophy is seen as an area of consistent decrease in circulation when compared to the opposite side.
Nerve injury
Nerve injury due to direct trauma or secondary to another injury or disease can affect blood flow and can be visualized with thermography.
Preventive medicine
Thermography also can be used to assess the vasculature and blood flow to tissues before and after exercise. Other uses include pre-purchase examinations, saddle fit, a training aid to avoid injury, pre-race examinations, hoof balance, following tendon healing after injury etc. As can be seen, there are many different uses for this non-invasive, but reliable diagnostic tool.
Frontline of Defense – Fight Against Swine Flu
Government and Corporations stay on high alert by activate measure in Public and Private sectors.
Health authorities say first locally contacted case of swine flu is inevitable and urge both public and private sectors to take precautions.
Many businesses start actively promote their adoption of precaution-measures to guarantee their business without being affect by the loss of confidence. For example hotels and restaurants, shopping center,tourism and luxurious cruise, entertainment facilities like casinos or horse-racing venue, offices and premises, many more.
Schools remain a particularly important consideration since outbreaks in Japan and the US originated in schools. Kindergarten, child care centre, primary schools, colleges and universities, also elderly and disabled homes, nurseries, hospitals are recommend to formulate plan to activate measures.
